HOST PLANTS:
This scale insect can infest all Juniper species, including Pfitzer and Savin. It also infests Cedars and Cypress.![]()
DAMAGE:
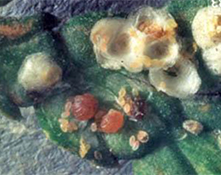
Infestation causes off-color foliage, yellowing and dieback of Juniper needles. Severely infested junipers may have little to no new growth. It takes close microscopic examination to detect these pests and to differentiate between juniper scale and spider mites. Close observation of infested foliage will reveal many white to brownish scale covers. Sooty mold fungus sometimes develops.
DESCRIPTION AND LIFECYCLE:
Adults appear as a small, circular, white scale with a yellow centre. Juniper scale overwinter as a mature female filled with eggs. The female then lays up to 40 eggs, starting in May. The eggs hatch in about 2 weeks and the yellowish crawlers seek a new site on the same host plant. Crawler emergence begins early to mid-June and continues over 30-40 days. They are light enough to be blown by wind to other hosts. The crawlers develop rapidly. They mate in late summer or early fall then the males disappear. There is only one generation per year.
CONTROL MEASURES:
Several parasitic wasps are among the natural enemies of Juniper scale. The Juniper scale is an armored scale which makes dormant oil treatments ineffective. The overwintering adult female is vulnerable. Treat the crawler stage with insecticidal soaps about mid-June and repeat as needed, starting when Catalpa is in full bloom.


Reference: Insects of Trees and Shrubs; Warren T. Johnson and & Howard H. Lyons, IPM Scouting Guide for Woody Landscape Plants; Rytlewski
